Advanced Bank Reconciliation in Dynamics 365 Finance encompasses the end-to-end bank reconciliation process, including statement importing, matching bank and company records, and report generation. With increased automation and enhanced functional capabilities, it significantly reduces the need for manual work and saves time for cash management clerks.
Advanced Bank Reconciliation in Dynamics 365 Finance encompasses the end-to-end bank reconciliation process, including statement importing, matching bank and company records, and report generation. With increased automation and enhanced functional capabilities, it significantly reduces the need for manual work and saves time for cash management clerks.
Let’s explore some of its key features:
- Importing Bank Statements: It supports a wide range of industrial standard bank formats as well as data entities.
- Automatic Matching: Upon importing the bank statement into the application, a matching engine operates in the background. Users can configure rules and criteria for matching transactions.
- Manual Matching: Following automatic matching, there may be transactions remaining for manual review and matching.
- Complete Reconciliation: Users are required to mark the bank reconciliation worksheet as completed. Subsequently, several batch jobs are triggered at the bank to execute tasks such as accounting or preparing necessary data for reporting.
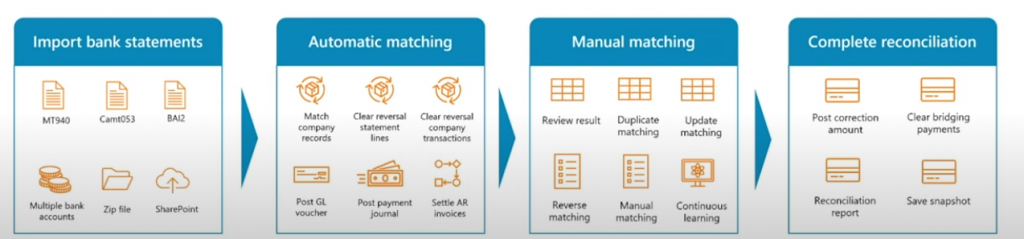
Dynamics 365 Finance’s Advanced Bank Reconciliation streamlines and enhances the reconciliation process, offering robust automation and functionality for efficient cash management.
Import Bank Statement
In addition to supporting electronic reporting and data entity frameworks (the latter slated for release in version 10.0.40), Dynamics 365 Finance offers compatibility with three industrial standard formats: Camt053, MT940, and BAI2.
Furthermore, for banks providing CSV or Excel formats, users can utilize data entity to seamlessly import them into the application. Various importing options are available, including manual creation, manual import, and periodically importing from a SharePoint folder (introduced in version 10.0.36).
It’s essential to consider certain import parameters, such as:
- Multiple bank accounts in one file
- Timezone conversion, which was enhanced and released in version 10.0.36.
This comprehensive support and flexibility in import options ensure seamless integration with diverse bank formats, facilitating efficient reconciliation processes within Dynamics 365 Finance.
Automatic Matching
The Automatic Matching feature in Dynamics 365 Finance encompasses three scenario groups:
- Matching with Company Transactions. Initially, the system supported matching one bank statement line with one company transaction. However, starting from version 10.00.36, it offers additional scenarios:
- Matching multiple bank statements linked with one company transaction.
- Matching one bank statement line with multiple company transactions.
- Matching multiple company bank statements with multiple company transactions.
- Posting New Entries from Bank Statement or Bank Reconciliation Worksheet. This scenario is applicable when a payment is not yet posted in Finance and Operations but appears in the bank statement first. The system supports various scenarios, including:
- Generating GL vouchers.
- Generating customer payment journals.
- Generating vendor payment journals.
- Settling open customer invoices.
- Clearing Errors. This functionality allows users to clear reversal company transactions and clear reversal statement lines.
These capabilities enhance the efficiency and accuracy of the reconciliation process within Dynamics 365 Finance, offering flexibility and comprehensive support for various matching and posting scenarios.
Match Bank Statement With Company Transactions
To automate matching, users can configure matching rules within Dynamics 365 Finance, by following these three steps:
- Define grouping conditions (bank statement line grouping conditions and company transaction line grouping conditions);
- Define matching rules (amount, date, unique number) and additional criteria like bank statement fields or company transaction fields;
- (optional) – define statement line scope (i..e bank statement fields + operator + values).
Settle Customer Invoices
This action within the system enables users to directly match bank statement lines with open customer invoices, facilitating automatic posting of payment journals and settlement of customer invoices. The process involves three steps:
- Find statement lines to define the scope. Not all your bank statements are custom payment-related.
- Match open invoices to define criteria (invoice number; sales order number; currency; also more fields are planned).
- Customer payment journal parameters to edit posting parameters on per legal entity basis (accounting date; method of payment; bank transaction type).
Generate Customer Payments
In cases where no custom invoice is found during the matching process, users can still utilize this section to post a custom payment journal without settling a specific invoice. Additionally, users have the option to enable the automatic settlement feature in the Accounts Receivable module, which facilitates automatic settlement based on criteria such as due date or invoice balance.
This set of features enables the settlement of custom payment journals based on criteria such as due date or invoice balance, leveraging existing functionality within the AR module. Users can utilize this criteria to settle invoices associated with the same customer account.
In this section, there are three steps as well:
- Find statement lines to define the scopes (bank statement fields; operator; values);
- In the “Match Invoices” step, which is optional, users have the capability to match the bank statement with customer invoices, encompassing both open and closed invoices. This flexibility is crucial because sometimes users may need to match transactions based on criteria such as customer name.
- Customer payment journal parameters whereas you can edit posting parameters on per legal entity basis (customer account; accounting date; method of payment; bank transaction type).



