Part and Global Address Book (also known as GAB) are Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations concepts that help to understand the relationships among people and organizations that are associated with your organization. For example, we can have a customer that can be also a vendor in a marketing campaign; or an employee in an organization who can also be a vendor.
In general, a party is a person or organization that is either internal or external to your organization. In F&O, each party has its own record in the application.
The overall idea of GAB is to have a single party to represent a person or organization, avoiding duplication of all these attributes.
Why Party Model in Dataverse?
Dual-write provides tightly coupled, biderictorial integration between Finance and Operations apps in Dataverse to ensure flawless harmonization of business processes between Dynamics 365 applications. Due to data integration mechanisms provided by Dual Write the data related to the party and the global address book can be synchronized in the database and Dataverse itself.
This model aims to add the global address book concept to Dataverse. But, the model is not only a Party table and includes updates on Account, Contact, Vendor, Addresses, and new ContactForParty, to unify DataModel between the two apps FO and DV.
Business Scenarios
Scenario 1
Let’s assume there is an employee (John) at Microsoft US who can log into the Microsoft US e-Commerce portal and purchase goods for personal use, which makes him both employee and customer.
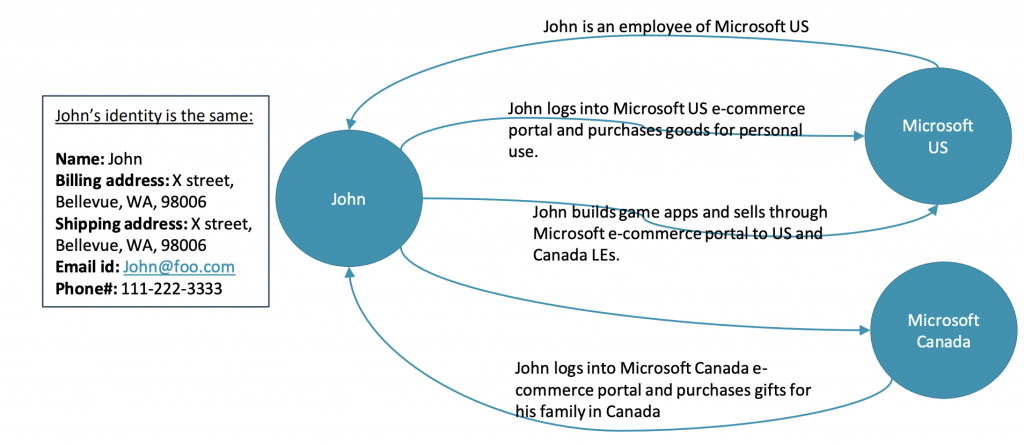
If you look at John as a person, he has some attributes which will not be changed. For example, the name of a person or an organization, and contact information (email, phone, etc.). He can also transact from both employee and customer/vendor perspectives. Therefore, the party ID will be the same but associated with the employee/customer/vendor accordingly.
In Global Economy, it is very much possible that a person or an organization can play more than one role in a business and switch roles based on the context.
Scenario 2
The next scenario is related to a big customer who can transact into many different legal entities and countries. From the customer perspective, the generic profile will stay the same: the first name of a person, organization name and etc. However, due to different countries, the nature of business, and legal entities – they have different taxonomy, i.e. payment terms.
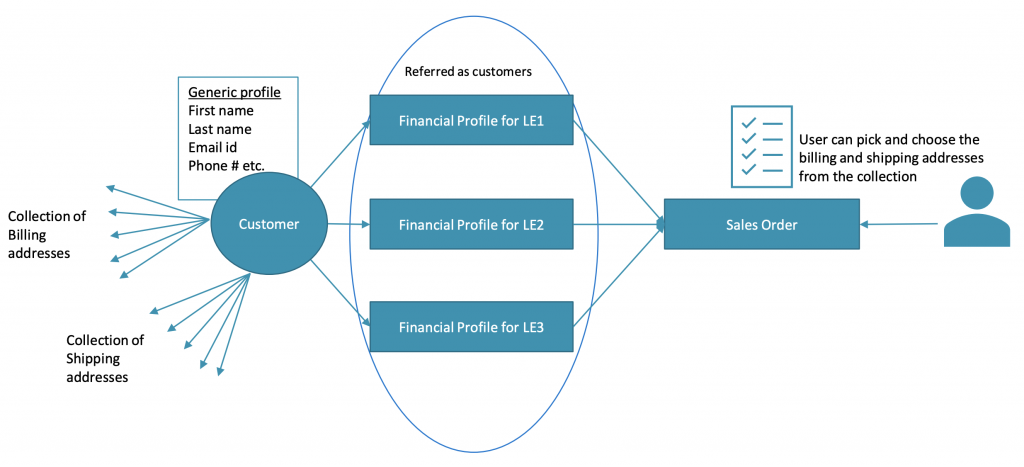
Therefore, you can consider a party with a generic profile. However, each legal entity will have a different financial profile. As a result, you will be able to create sales orders against these financial profiles in each legal entity.
Now, there is an ability to have separate generic profiles for a specific person or an organization as well as the ability to store and retrieve as many addresses as possible for each type of transaction.
Then, you can have various financial profiles that are referred as a customer or vendor.
Scenario 3
There could be scenarios with a combination of customers becoming an organization if that organization has multiple locations and there are specific clients of each location.
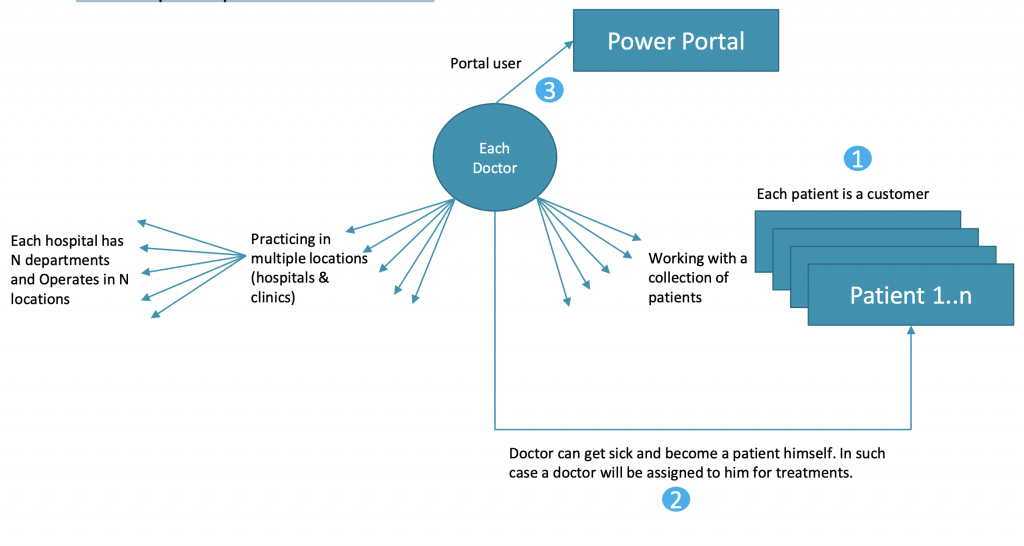
Due to COVID, let’s take a hospital scenario, where a doctor treats one or more patients at the same time. Each patient is referenced based on the doctor he/she is assigned to. Also, Doctors can log in to the hospital website and track the patient records and give directions towards prescriptions and treatments.



